Data Communication Network
Data communications are the exchange of data between two devices using one or multiple forms of transmission medium using one of the three transmission modes. That is, data communication is movement of data from one device or end-point to another device or end point through electrical or optical medium. Systems that facilitates this movement of data between devices or end-points are called data communication network. There are 5 components of a data communication network. The devices which are in need to be a part of a data communication network made up of computer hardware and software.
I encourage you study the book Data Communications and Networking with TCP IP Protocol Suite 6th Edition by Behrouz A Forouzan
Read More: 3 Criteria Necessary for an Effective and Efficient Network
Data communication networks collect data from devices such as microphone and let the data to be carried to the receiver or destination such as a micro-computer or minicomputer. However, it could be the opposite, that is data communication networks can also carry data from a micro-computer or minicomputer to a device such as printer. Data communications networks facilitate more efficient use of computers and improve the day-to-day control of a business by providing faster information flow. They also provide message transfer services to allow computer users to talk to one another via electronic mail, chat, and video streaming.
Read More: 4 fundamental characteristics of data communication system.
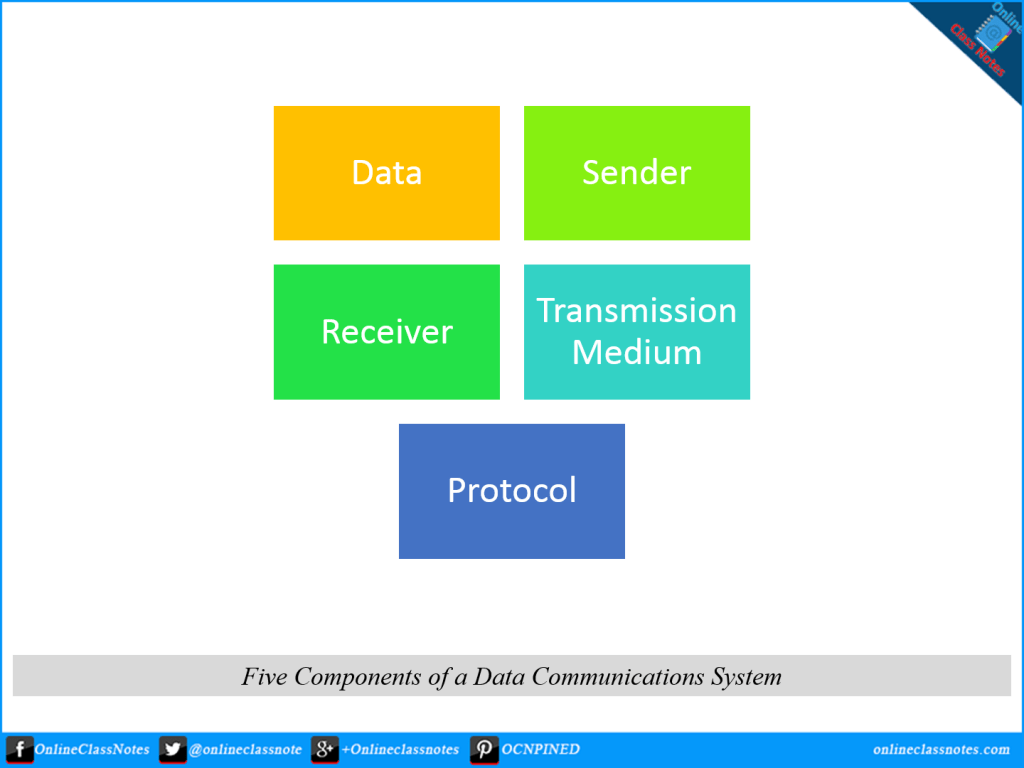
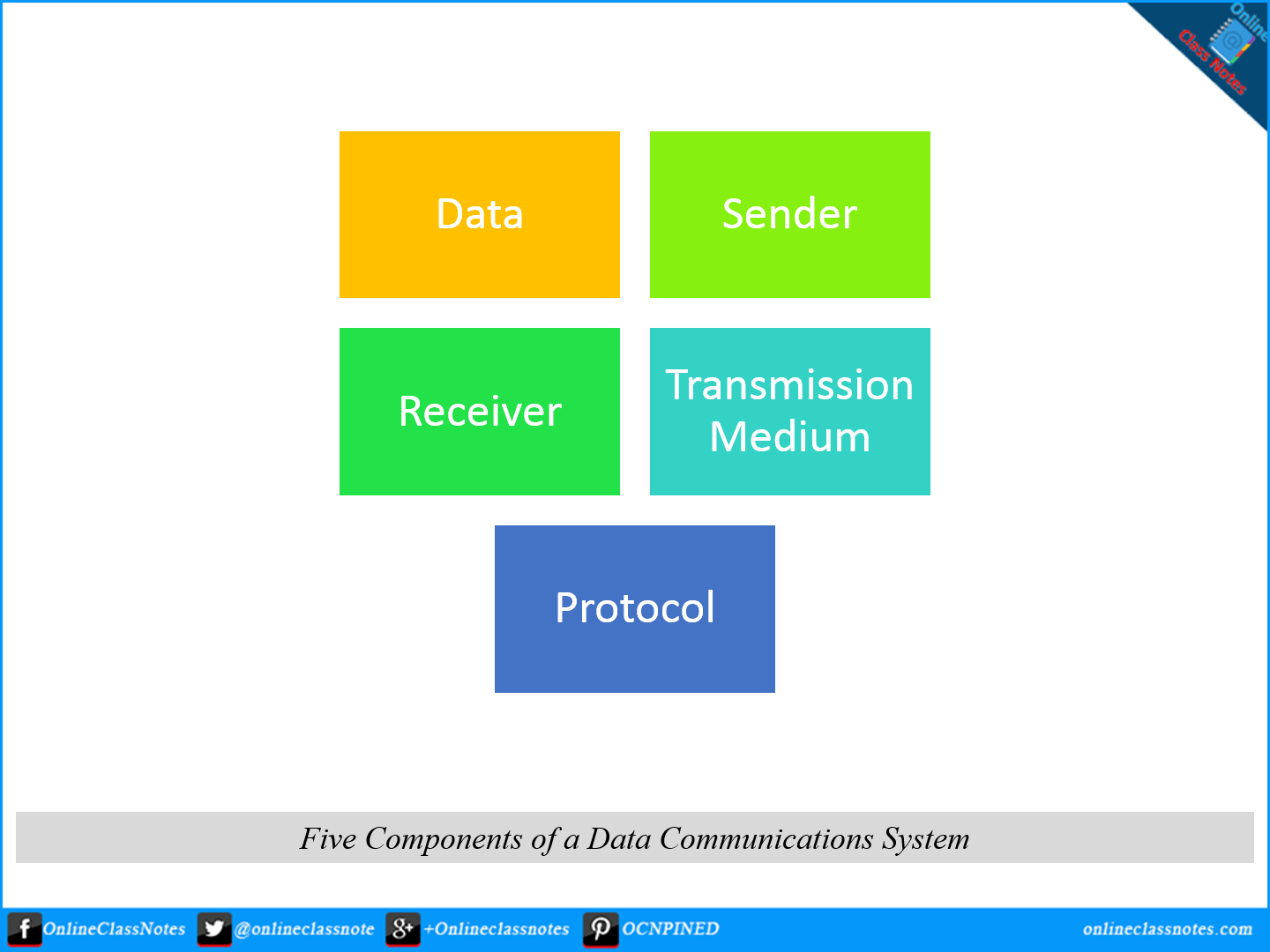
5 components of data communication network
- Data
- Sender
- Receiver
- Transmission Medium
- Protocol
1. Data
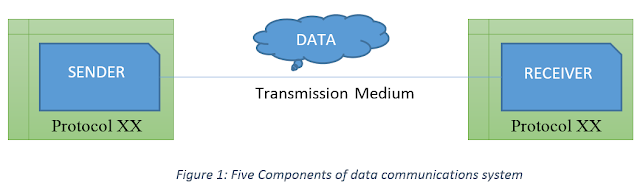
Communication of data means a message or data will be transmitted from one device and will be received in the destination or target device. Thus the first component in a data communication network is data or message to that needs to be delivered and received. Data or message can be of various forms such as text, audio, video, image or combinations of these forms etc.
Read More: What is Data and Information? Write the differences between Data and Information.
2. Sender
A source must send that to a destination. This source is the sender. The device that sends the data to the destination or target is the Sender. It can be a computer, cell phone, video camera and so on.
3. Receiver
The destination of a transmitted data is the receiver which will receive the data. The device that receives the data is the Receiver. A receiver can again be a computer, cell phone, video camera and so on.
4. Transmission medium
In data communication network, the transmission medium is the physical path for the data to travel to its destination. Receiver receives the data at one end of this path and the sender sent from another end of the path. Transmission medium could be like twisted-pair cable, coaxial cable, optical fiber cable etc.
Read More: What are the advantages and disadvantages of optical fiber?
5. Protocol
A protocol is nothing but a set of rules that applies on the full data communication procedure. This is like an agreement between the two devices to successfully communicate with each other. For example, how to send the data, how the data will be traveling, how to ensure that full data has received, how to handle errors in transmission etc. Both devices follow the same set of rules or protocol so that they understand each other.