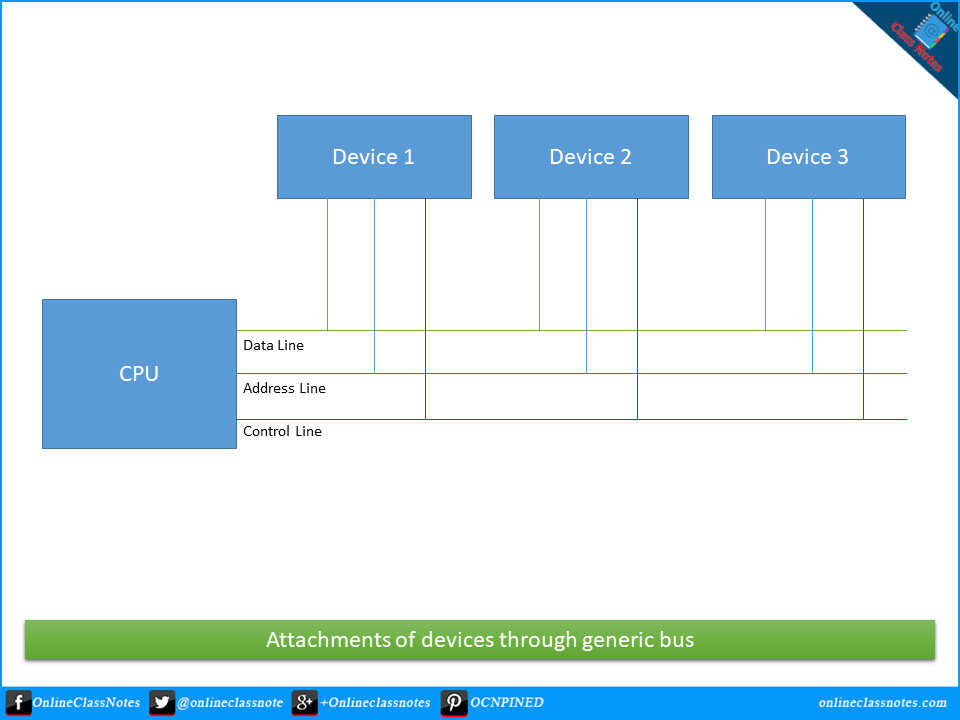
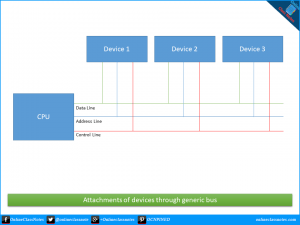
Bus:
Bus is an electrical path that resides inside the motherboard. There are two main types of bus; internal or system bus and external or expansion bus. The system bus connects the CPU to other devices and the expansion bus connects the external devices such as keyboard, mouse etc. to the CPU. The three main parts of the bus are control lines, address lines and data lines.
i) Data Lines:
The meaningful data which needs to be sent or received from a or to a device is placed onto these lines.
ii) Address Lines:
This allows CPU to reference certain memory locations within the memory
iii) Control Lines:
These allow the CPU to control which operation the attached devices should perform, such as read or write.
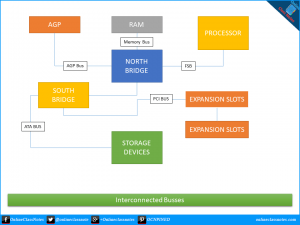
Bus Speed:
A bus is simply a circuit that connects one part of the motherboard to another. The more data a bus can handle at a time, the faster it allows information to travel. The speed of the bus, measured in megahertz (MHz), refers to how much data can travel across the bus simultaneously.
Bus speed usually refers to the speed of the front side bus (FSB), which connects the CPU to the Northbridge. FSB speeds can range from 66 MHz to 800 MHz. Since the CPU reaches the memory controller through the Northbridge, FSB speed can dramatically affect a computer’s performance.