Parallelism in CPUs refers to the ability of a processor to perform multiple tasks simultaneously, thereby increasing throughput and overall performance. Parallelism can be achieved at different levels within a CPU, from the execution of individual instructions to the concurrent execution of multiple threads or processes.
Microprocessor and Computer Architecture
How does pipelining improve CPU performance? What are the stages of the pipeline, and what challenges may arise in implementing pipelining?
Pipelining is a technique used in CPU design to improve performance by overlapping the execution of multiple instructions. It allows the CPU to process several instructions simultaneously, thereby increasing throughput and overall efficiency.
Describe the architecture of a modern CPU, including its major components such as ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit), control unit, registers, and cache memory.
The architecture of a modern CPU (Central Processing Unit) is designed to efficiently execute instructions and process data.
Discuss the role of instruction-level parallelism (ILP) in CPU design. What techniques are used to exploit ILP, and what are their limitations?
Instruction-Level Parallelism (ILP) is a crucial concept in CPU design aimed at improving performance by executing multiple instructions simultaneously or overlapping their execution. ILP allows CPUs to exploit available instruction-level parallelism within a program to increase throughput and reduce execution time.
Explain the purpose and function of CPU caches. What are the different levels of cache memory, and how do they impact CPU performance?
CPU caches serve as high-speed storage units that store frequently accessed data and instructions to reduce the latency of memory access and improve overall CPU performance. Caches are designed to exploit the principle of locality, which states that programs tend to access a relatively small subset of data and instructions repeatedly within a short period of time. By storing this frequently accessed data and instructions in caches, CPUs can minimize the time spent waiting for data to be fetched from slower main memory.
What are the differences between RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computing) and CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computing) architectures? Discuss their advantages and disadvantages.
RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computing) and CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computing) architectures are two distinct approaches to CPU design, each with its own characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages.
What is CPU? What are the 10 functions of CPU?
CPU (Central processing unit)
A CPU, or Central Processing Unit, is the main component of a computer system that performs the majority of processing tasks required by the system. It is often referred to as the “brain” of the computer. The CPU is responsible for executing instructions, performing calculations, managing memory, and controlling input and output operations.
The CPU consists of three main components: the control unit, the arithmetic and logic unit, and the registers. The control unit is responsible for managing the flow of instructions between the CPU and other components of the computer system, including memory, input/output devices, and other processors. The arithmetic and logic unit performs mathematical and logical operations, such as addition, subtraction, and comparison of values. The registers are small areas of memory used to store data and instructions that the CPU is currently working on.
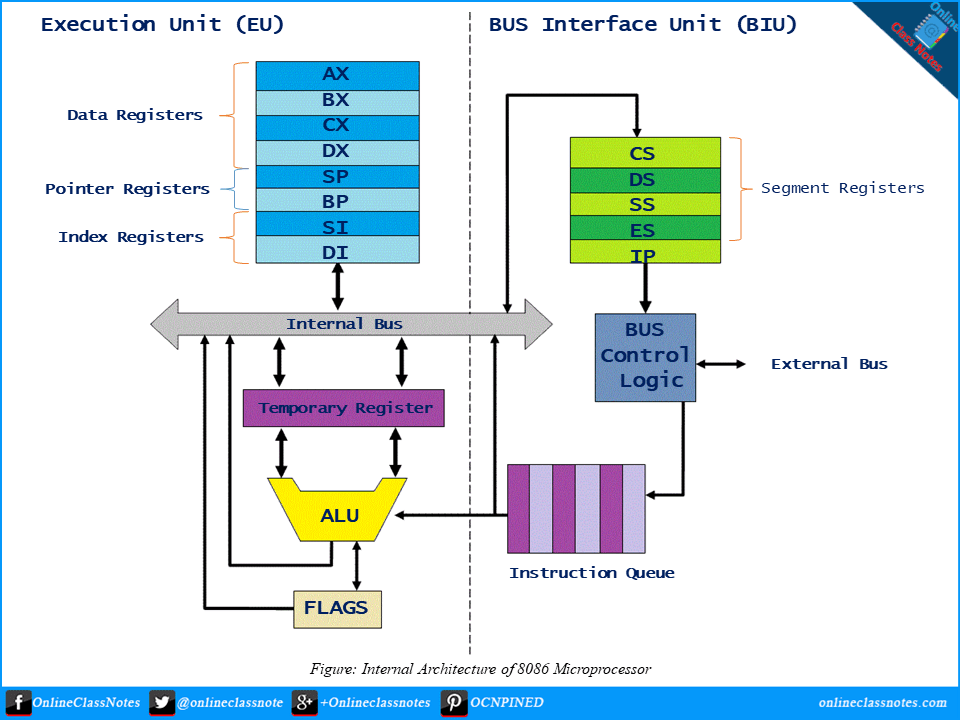
Describe the Internal Architectures, Features, Working Principles and Registers of 8086 Microprocessor.
Internal Architecture of Intel 8086 Microprocessor The Intel 8086, also called the iAPX 86, is a 16-bit microprocessor designed by Intel Corporation in between 1976-1978. This Intel 8086 microprocessor gave rise to the x86 architecture or 16-bit architecture. The figure given below is the internal architecture of Intel 8086 microprocessor Features of 8086 Microprocessor: 8086 … Read more
What are the 6 steps followed by CPU in computer to Execute an Instruction?
CPU (Central Processing Unit)
CPU or central processing unit in computer is an electronic circuitry that carries out the instruction given by a computer program. CPU in computer execute instruction by performing basic arithmetic, logical, control and I/O operations as required per instruction. CPU in computer is considered to be the brain of the computer. The speed and efficiency of a computer mostly depends on it’s CPU.
Define Instruction Set Architecture. What are the main objectives of ISA in computer systems.
Instruction Set Architecture (ISA): An instruction set is the interface between a computer’s software and its hardware, and thereby enables the independent development of these two computing realms. ISA is the set of basic instructions that a processor understands. ISA includes functional definition of operations, modes, and storage locations supported by hardware and precise description of … Read more