The architecture of a modern CPU (Central Processing Unit) is designed to efficiently execute instructions and process data.
general purpose registers
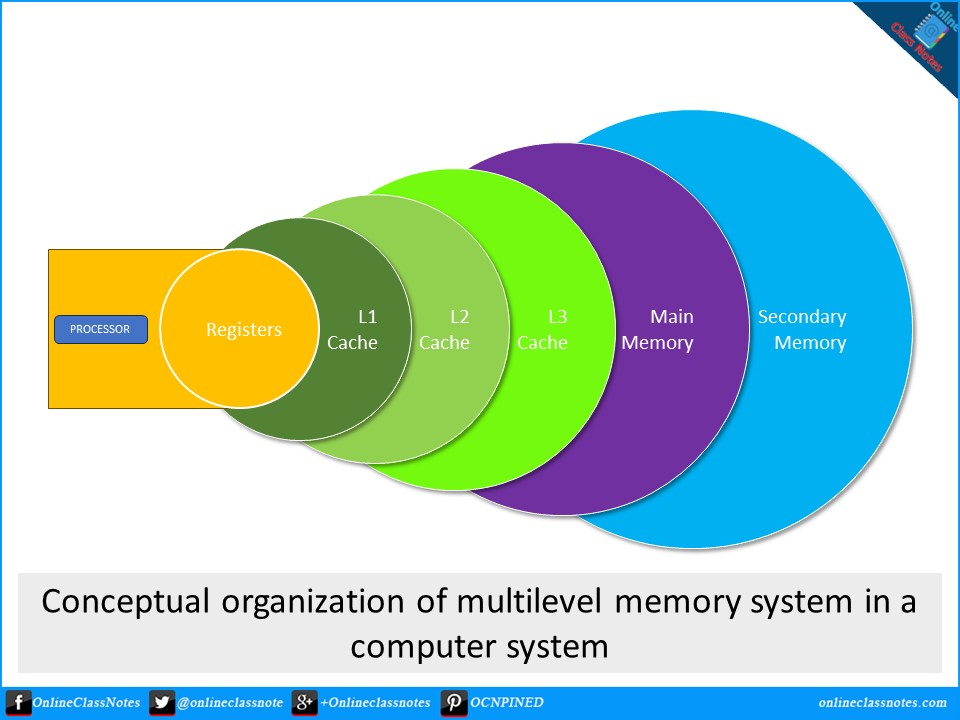
Explain the conceptual organization of multilevel memory system in a computer system.
Multilevel Memory Systems
For a CPU to perform at its maximum potential, it needs rapid and continuous access to memory. However, high-speed memory is costly, which necessitates the use of various levels of memory that balance performance and cost. Here’s an overview of the different types of memories in a computer system and their organization in a multilevel memory hierarchy.
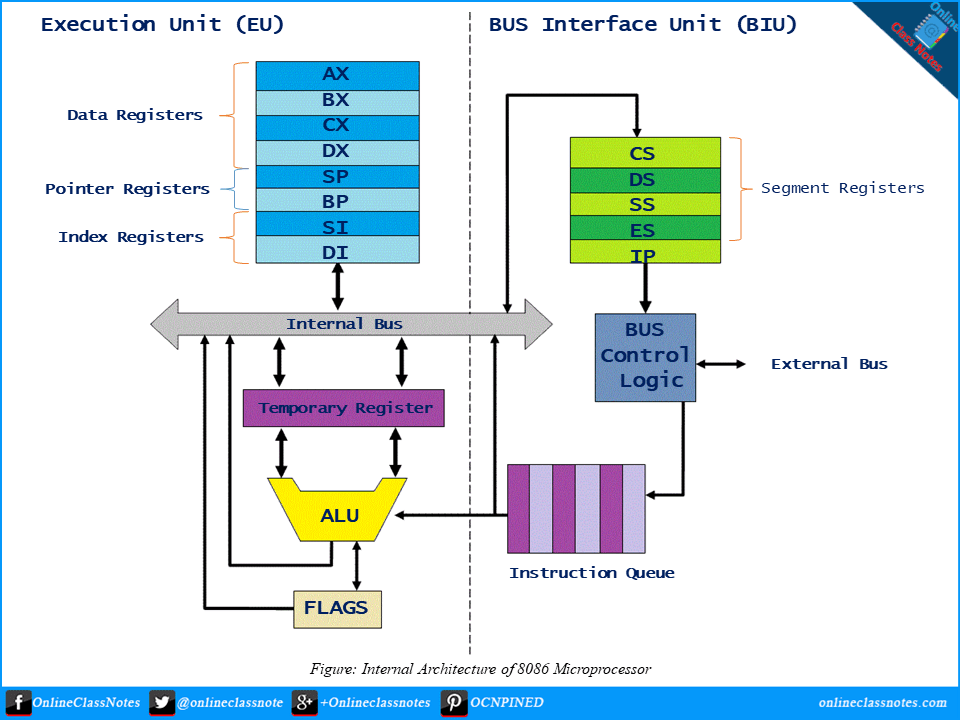
Write short notes on general purpose registers (AX,BX,CX,DX,SP,BP,SI,DI) and ALU in Intel 8086 microprocessor
General Purpose Registers
In computer architecture, registers in processors are quickly accessible locations available to a computer’s central processing unit (CPU). Registers usually consist of a small amount of fast storage, although some registers have specific hardware functions, and may be read-only or write-only. Registers are normally measured by the number of bits they can hold, for example, an “8-bit register”, “32-bit register” or a “64-bit register” (or even with more bits).