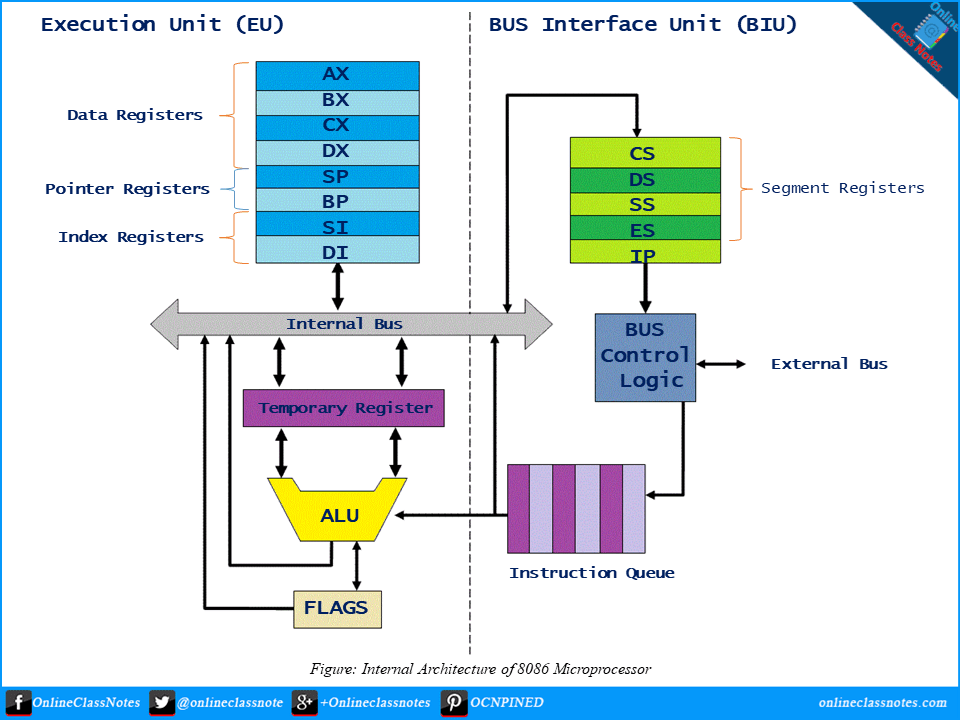
Purposed of Segment Registers
CS (Code Segment)
Code segment (CS) is a 16-bit register containing address of 64 KB segment with processor instructions. The processor uses CS segment for all accesses to instructions referenced by instruction pointer (IP) register. CS register cannot be changed directly. The CS register is automatically updated during far jump, far call and far return instructions.