Computer systems reached today’s modern age step by step, these steps are called generations. In each generation computers with new features and functions starts to get the market and the older computers slowly gets replaced. IBM company started categorize the development of computers into generations, though not everyone in the industry including users will be agree on the periods of each generation. However, based on the use of electronic devices, computers systems can be categorized into following generations so far.
Generations of Computer
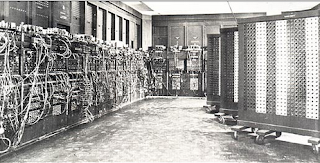
First Generation (1951 – 1959)
Vacuum tubes were used to build computers of this generation. These computers were so large in size because of using thousands of diode, triode, transistors, capacitors etc. and also used to use lot of electricity. These computers of this generation used produce a lot of heat, so those were more expensive to support by setting up cooling systems. Maintenance of these huge sized computers were complex and expensive. Following are some of the characteristics of the computers of first generation.
10 Characteristics of First Generation of Computers
- Use of vacuum tubes to make circuits
- Use of magnetic drums
- Use of machine language and symbols in instructions
- Very small amount of storage space
- Use of punch cards as I/O devices
- Huge in size and poor in mobility
- Very slow and less reliable output
- Use of high electricity
- Generates too much heats
- Complex and expensive to maintain
Example: UNIVAC I, IBM 650, MARK II, MARK III etc.
Second Generation (1959 – 1971)
In 1947 transistors were invented, which was used in second generation computers to reduce the heat and size problem of the computers from first generation along with following characteristics
8 Characteristics of Second Generation of Computers
- Use of transistors
- Magnetic memory and magnetic storage disks
- High speed I/O devices
- Invention and use of high level languages such as Fortran and Cobol.
- Reduced size
- Solution to heat generation
- Communication by using telephone line
- Improvement of speed and reliability
Example: Honeywell 200, IBM 1620, IBM 1400 etc.
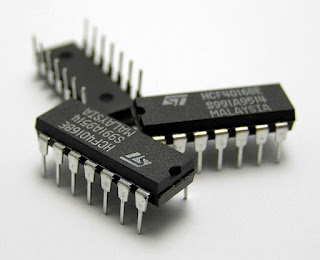
Third generation (1965 – 1971)
Use of integrated circuits (IC) started the third generation of computer. IC reduced the size, price, use of electricity etc. IC also facilitates speed and reliability of computers. Development of IC enabled organizing the whole central processing unit in single chip. Use of monitor also started in this generation. Operating system was improved to a new level and high speed line printers were in use. Followings are some of the characteristics of third generation.
10 Characteristics of Third Generation of Computers
- Use of Integrated Circuits (IC) instead of transistors
- Use of Semi-conductor memory
- Small size than previous generation computers
- Use of magnetic storage devices
- Improved faster operations and more dependable output
- Use of mini computers
- Use of monitors and line printers
- Use of high level programming languages
- Less expensive than 2nd generation computers
- Less expensive maintenance cost
Examples: IBM 360, IBM 370, PDP-11 etc.
Fourth generation (1971 – present)
The computers that we use now-a-days are the computers from fourth generation. From this generation more use of semi-conductors in memory started. Microprocessors has been created with LSI (Large Scale Integration) and VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration). The size and price of computers has both been reduced to significant levels. Followings are some of the characteristics of computers from fourth generation.
10 Characteristics of Fourth Generation of Computers
- Microprocessor based system that uses Very Large Scale Integrated (VLSI) circuits.
- Microcomputers became the cheapest at this generation.
- Hand-held computer devices became more popular and affordable
- Networking between the systems was developed and became of every day use in this generation.
- Storage of memory and other storage devices has increased in big amount.
- Outputs are now more reliable and accurate.
- Processing power or speed has increased enormously.
- With increment in the capacity of the storage systems large programs were started to be in use
- Great improvement in the hardware helped great improvement in the output in screen, paper etc.
- Size of the computer devices became such small that even desktop computers were easily movable along with portable computers such as laptops etc.
Example: IBM 3033, Sharp PC – 1211 etc.
Fifth generation (future)
Computers from fourth generation are in use of everyday work. Fifth generation computers are from the future. Actually the computers from fifth generation are already in use under limited exposure and not available for everyone to try as the development process is still ongoing. A few of the characteristics of those fifth generation computers are already in practice or available in the fourth generation computers but those are either not complete nor available for everyone. Following are some of the characteristics of fifth generation computers.
10 Characteristics of Fifth Generation of Computers
- Multi-processor based system:
- Currently we use one processor per CPU though there are special computers already in use with parallel computing but those are very limited and not complete.
- Use of Artificial Intelligence: AI is also in use already, but still it is in development. In fifth generation computers, we expect to see AI applied in everywhere, from navigating to browsing, from everyday word-excel sheet processing to heavy duty image processing and video analyzing etc. AI will become personal assistant, AI will automate almost every aspect computing.
- Use of optical fiber in circuits
- Development of the elements of programs
- Automated audio in any language to control the workflow of the computer
- Magnetic enabled chips
- Huge development of storage: Already we have SSD storage which is way faster than HDD, and a few other technologies under development, thus we expect to faster and larger storage in fifth generation computers.
- More powerful micro and macro computers
- Development of enormous powers with AI