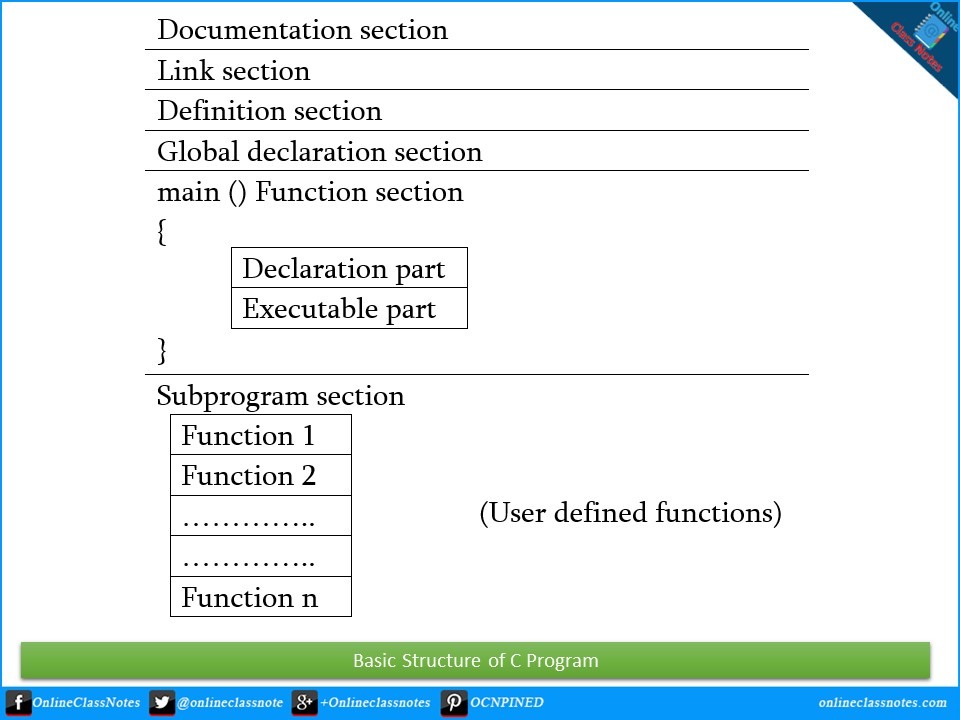
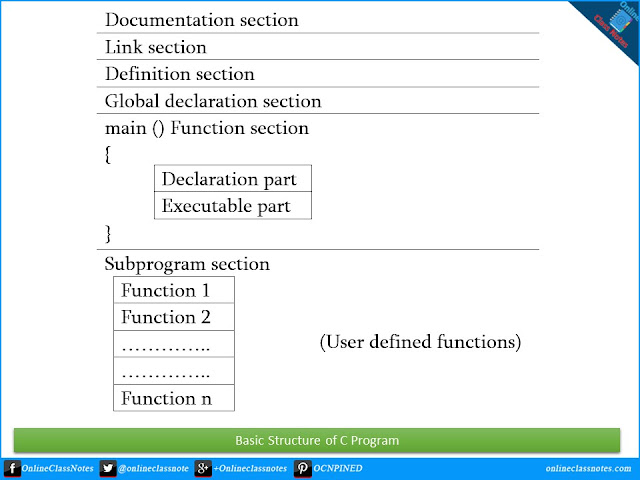
Basic structure of C programming
To write a C program, we first create functions and then put them together. A C program may contain one or more sections. They are illustrated below.
Bored with Text? Watch the video instead.
Documentation section
The documentation section consists of a set of comment lines giving the name of the program, the author and other details, which the programmer would like to use later.
Link section
The link section provides instructions to the compiler to link functions from the system library such as using the #include directive.
Definition section
The definition section defines all symbolic constants such using the #define directive.
Global declaration section
There are some variables that are used in more than one function. Such variables are called global variables and are declared in the global declaration section that is outside of all the functions. This section also declares all the user-defined functions.
main () function section
Every C program must have one main function section. This section contains two parts; declaration part and executable part
Declaration part
The declaration part declares all the variables used in the executable part.
Executable part
There is at least one statement in the executable part. These two parts must appear between the opening and closing braces. The program execution begins at the opening brace and ends at the closing brace. The closing brace of the main function is the logical end of the program. All statements in the declaration and executable part end with a semicolon.
Subprogram section
If the program is a multi-function program then the subprogram section contains all the user-defined functions that are called in the main () function. User-defined functions are generally placed immediately after the main () function, although they may appear in any order.
All section, except the main () function section may be absent when they are not required.
Following is a sample C Program that contains all of the above mentioned sections In this above sample C Program.
If you can not see the code, then please click this link to view code
- Line 1-7: These are comments, these lines will not be executed. This is the Documentation Section.
- Line 10: This is the Link Section. Here we are linking our program to a header file or library called
stdio.h, this library provides methods for sending output to screen or taking input from user using standard output and input devices. - Line 13: This is the Definition Section. Here we are defining a constant.
- Line 16 & 19: This is Global Declaration Section. In line 16 we are declaring a global variable and in line 19 we are declaring an user defined function
- Line 21-35: This is the Main Function Section. Every C Program must have this section. This section can have two sub-sections. Declaration Part and Executable Part. However, this two parts can be mixed. In line 23 we are declaring local variable. Line 26, 29, 32 and 34 are executable statements.
- Line 37-39: This is the Sub-Program Section. Here we have defined an user defined function that we have previously declared in the Global Declaration Section.
Must Read:Draw the flow chart of the process of compiling and running a C program