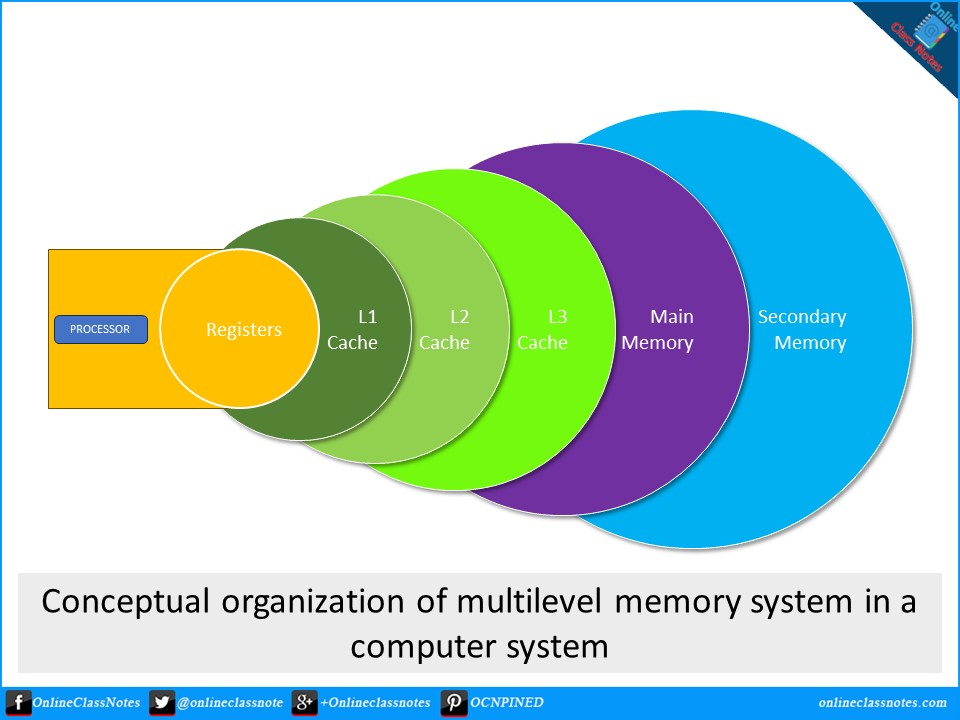
Multilevel Memory Systems
For a CPU to perform at its maximum potential, it needs rapid and continuous access to memory. However, high-speed memory is costly, which necessitates the use of various levels of memory that balance performance and cost. Here’s an overview of the different types of memories in a computer system and their organization in a multilevel memory hierarchy.