Bus Topology
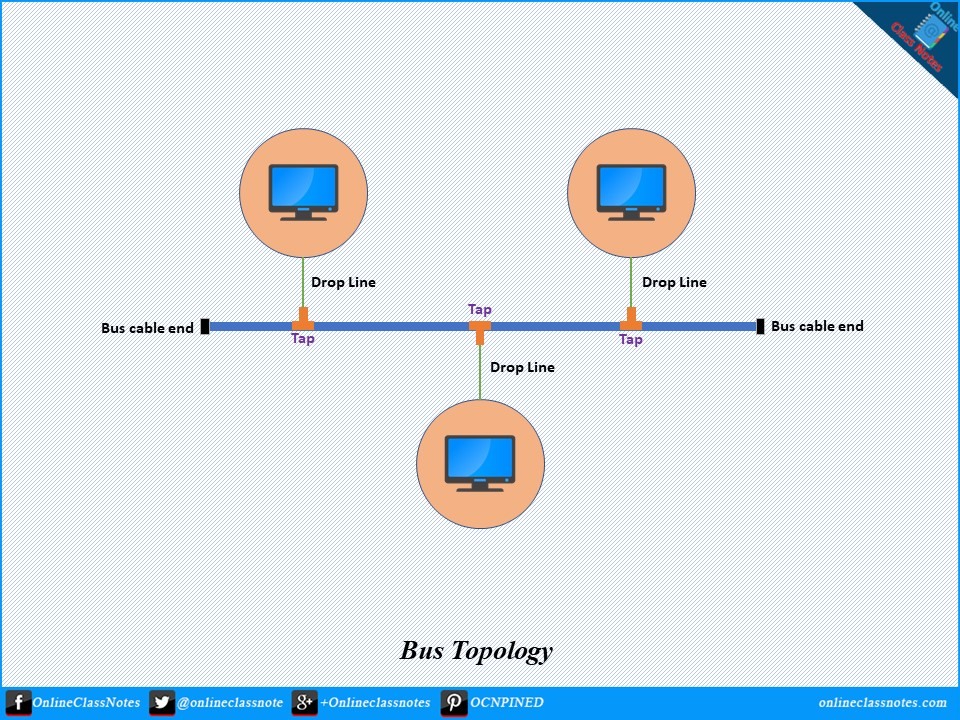
Unlike star topology or mesh topology, a bus topology is a multi-point connection between the nodes or devices on the network. A long cable works as backbone of the network. All the different nodes in the network connects at different points on the main cable. A connection point in the main cable for a node or device is the nearest point for the node.
It can be a little confusing with star topology. In star topology, nodes connect to a central device which makes the data communication between devices by receiving and sending data from sender to receiver. But in bus topology, though the nodes connect to a single main cable, there is no such controller like a hub. Instead, devices or nodes do their routing.
Each node connects to the main cable using a drop line and a tap. A drop line is a connection cable between a node and the main cable. A tap is a connector that either splices the main cable and let the drop line connects to the main cable, or it punctures the sheathing of the main cable to make contact with the metallic core.
Advantages of bus topology
- Easy installation of nodes.
- Bus offers less cabling than star or mesh topology. Its because, the main cable can be placed in close contact to each node and then nodes will require small length drop lines to connect to the main cable.
- Bus also eliminates the redundancy. All nodes shall not have long length connection cable to a certain point or hub, as in start topology. Instead, only the main cable stretches through the entire facility.
Disadvantages of bus topology
- As a signal travels along the backbone, some of its energy is transformed into heat. Therefore, it becomes weaker and weaker as it travels farther and farther. For this reason there is a limit on the number of taps a bus can support and on the distance between those taps.
- It is difficult to add new devices to the main cable. As distance between taps are calculated at the beginning and placing a new device can cause degradation in quality
- Fault isolation is difficult
- Signal reflection at the taps can cause degradation of quality
- A fault or break in the bus cable stops all transmission, causing the full network failure
Read More
