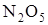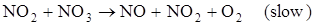Order:
Order of a reaction is defined by the number of atoms or molecules, whose concentration change during the reaction and determine the rate of the reaction.
For example,
It is a first order reaction.
It is a second order reaction.
Molecularity:
The molecularity of an elementary reaction is defined as the number of reactant molecules involved in a reaction. Such as,
|
Reaction
|
#
|
Molecularity
|
|
i
|
1
|
|
|
ii
|
2
|
|
|
iii
|
3
|
The molecularity of a complex reaction may be defined as the number of molecules or atoms taking part in the rate-determining steps. Such as, the decomposition of 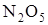 occurs by the following steps.
occurs by the following steps.
Step 1 + Step 2 + Step 3:  (overall reaction)
(overall reaction)
Here, step 2 is rate determining and has molecularity ‘2’, which could be considered as the molecularity of the decomposition reaction of